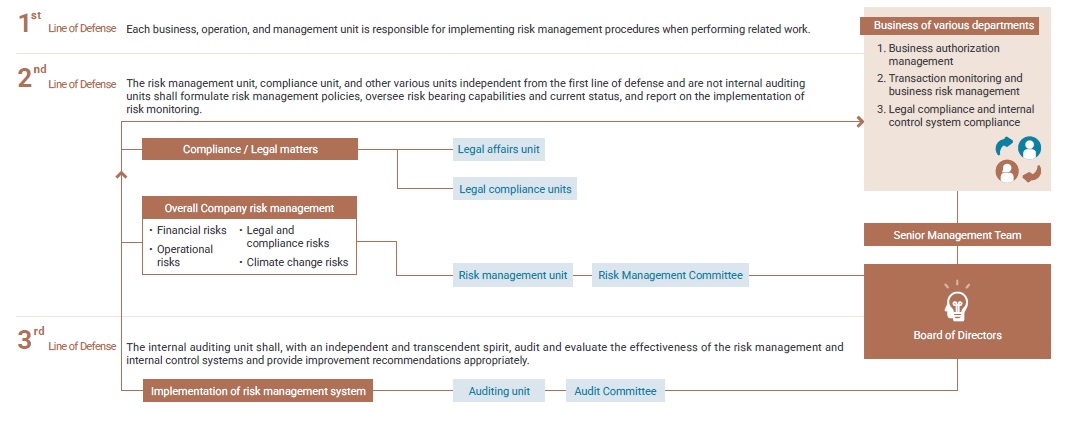
Yuanta Financial Holdings’ risk management structure covers the board of directors, the Risk Management Committee, senior management, each unit, risk management units, compliance units and other risk management related units, and internal auditing units.
- Investor Relations
- Corporate Governance
- Risk Management
The board of directors holds ultimate responsibility for risk management regarding all operations. Its major duties include approval of the Company’s risk management policy and risk management systems, approval of annual risk limits and thresholds for monitoring indicators, and supervision of the implementation of the Company’s risk management systems.
The Risk Management Committee assists the board of directors in overseeing the operational mechanisms related to risk management. Its main responsibilities include reviewing risk management policies and systems, reviewing annual risk limits and thresholds for monitoring indicators, reviewing reports on risk management implementation, overseeing the management of the Company’s existing or potential risks, and assisting the board of directors in overseeing the implementation of risk management decisions.
Senior management monitors risks associated with all Company business operations, and ensures that the Company’s risk management system can completely and effectively control all relevant risks.
Each unit identifies and manages the risks arising from the functions or scope of responsibilities under its control, and designs and implements effective internal control procedures to address the characteristics of such risks, so as to fully cover the risk management functions of the relevant operational activities.
Risk management units, compliance units, and other risk management related units establish risk management mechanisms for each major risk category, monitor overall risk-bearing capacity and risk-bearing status, and report on the status of monitoring and control implementation.
Internal auditing units, in an independent and above board spirit, check and evaluate whether the risk management and related internal control systems are operating effectively and efficiently on a continuous basis, and provide recommendations for improvement in a timely manner.
As global financial environments continue to evolve, the risks faced by the financial industry have become increasingly diverse and complex. In response, the Company strives to strengthen corporate governance and risk management procedures, including risk identification, measurement, monitoring, reporting, and response. Through cross-departmental integration, risk management mechanisms are embedded into decision-making oversight and daily business operations. A comprehensive "three lines of defense for risk management" is established to effectively identify and measure the level of risks and monitor and manage them, so as to reduce the frequency and impact of risks.
In order to establish the Company’s risk management standards, and ensure that its risk management is comprehensive, effective, and reasonable, Yuanta has set in place its risk management policy to serve as guiding principles for its risk management system. The Company’s risk management systems shall adhere to this policy, and shall be set after taking into consideration the various risk attributes faced and their potential impact on the Company’s operational stability and capital security.
The Company’s risk management system shall cover company-wide major business risks, including financial risk, operational risk, legal and compliance risk and climate change risk. Subsidiaries shall establish a risk management system in accordance with the Company’s risk management policy and the regulations of the local competent authorities that is consistent with their business portfolio, business scale, and capital size in order to effectively manage the various risks they undertake.
The main categories and elements of financial risks are set out below:
Market risk refers to the risk of loss on valuation of the Company’s financial positions due to changes in market prices, volatility or correlation, including indexes, stock prices, interest rates, exchange rates, commodities or credit premiums.
Credit risk refers to the risk of loss arising from the following situations:
a. Instances in which a bond (bill) issuer, borrower, counterparty, or custodian violates their contract, experiences bankruptcy or liquidation, or otherwise fails to uphold their contractual obligation to discharge debt liabilities, resulting in the risk of loss.
b. Instances in which a bond (bill) issuer, borrower, or counterparty’s guarantor violates their contract, experiences bankruptcy or liquidation, or otherwise fails to uphold their contractual guarantee liabilities, resulting in the risk of loss;
c. Instances in which the underlying instrument of a financial product experiences weakened credit or has its credit rating reduced, or in which the issuance contract of a financial product is violated, resulting in the risk of loss.
Market liquidity risk refers to insufficient market trading volume continuity or market disorder leading to a clear decline in trading volume, causing asset sales or closure of positions currently in progress to face the risk of potential loss.
Liquidity risk refers to the risk that the Company will not be able to meet its various payment obligations due to an imbalance in its financial structure caused by improper capital planning or the inability to obtain sufficient funds in a timely manner through asset sales or external financing due to significant changes in the general economy or financial markets.
Asset-liability matching risk refers to the risk of unfavorable changes in the Company’s overall profit or loss, or net interest income, or net worth due to changes in interest rates or exchange rates as a result of differences in the valuation currencies, interest accrual methods, or maturity periods of interest-bearing assets and interest-bearing liabilities.
Large exposures represent the risk that, due to the concentration of the business on a specific risk factor, there may be a material loss to the Company as a result of an unanticipated change in that specific risk factor.
Insurance risk refers to the risk of loss due to unexpected changes when operating an insurance business and assuming the transferred risks of the insured after collecting insurance premiums and paying claims and related expenses in accordance with the contract.
Operating risk refers to the risk of loss arising directly or indirectly from negligence or errors in internal operations, staff or systems, or from external events.
The main categories and elements of operational risk are set out below:
Information security risk refers to the extent to which the normal operation of business-related information systems is affected or jeopardized by improper use, leakage, tampering, or destruction of information assets due to human negligence, intentional, or natural disasters.
Human resources risk refers to the risk related to human rights issues of employees and the development and management of human resources of the Company, such as attracting, retaining, and developing talents.
Emerging risks refer to new types of business or new types of risks that may have adverse effects on future business operations due to the failure to identify and evaluate risks.
Integrity management risk refers to the risk that a director of the board, supervisor, manager, employee, or person with substantial control over the Company will directly or indirectly offer, promise, request, or receive any improper benefit or commit other unethical conduct such as breach of good faith, wrongfulness, or breach of fiduciary duty in the course of engaging in business activities in order to obtain or maintain benefits.
Reputation risk refers to the risk of loss resulting from termination or interruption of business due to negative evaluation by the media or the public.
Strategy risk is the risk resulting from inappropriate strategies or changes in the Company’s operational environment.
The main categories and elements of legal and compliance risk are set out below:
Compliance risk refers to the risk of incurring penalties from the regulatory authorities, resulting in significant financial or reputational loss, when the Company engages in business activities without fully complying with relevant laws and regulations.
Legal risk refers to the risk of potential loss resulting from invalidation of the contract due to its lack of legal validity, ultra vires acts, omission of terms and conditions, and inadequate regulations.
Risks of money laundering and financing of terrorism refer to the risk that the business is abused for money laundering or financing of terrorism activities.
Climate change risk refers to the potential risk arising from climate change or the mitigation of climate change, including the risk of climate change in investment and financing and the risk of climate change in the Company’s own operations:
a.Investment and financing climate change risk refers to the potential risk that may increase to the Company due to the impact of climate change by issuers, counterparties, or financing customers that have investment or financing business dealings with the Company or its subsidiaries.
b.The climate change risk of the Company’s own operations refers to the potential risk to the Company’s own operations that may increase due to the impact of climate change on the Company’s or its subsidiaries’ own basic operational infrastructure or the process of low-carbon transformation.
With the increasing global regulatory requirements, the rapid development of emerging technologies and the threat of climate change, risk management in the financial industry will change dramatically in the future. In order to address this trend as early as possible, the Company has completed the identification of emerging risks and subsequent plans and actions to further improve the efficiency and effectiveness of risk control.

 元大金控
元大金控